- Home >> News >> Blog articles >> Internet of things
RFID Internet of Things Technology Solution
1. What is radio frequency identification?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless communication technology that can identify specific targets and read and write related data through radio signals without establishing mechanical or optical contact between the identification system and specific targets. The most important advantage of radio frequency identification is non-contact identification, which can read tags through snow, fog, ice, paint, dirt and harsh environments where barcodes cannot be used, and the reading speed is extremely fast, in most cases less than 100 milliseconds.
The advantage of radio frequency identification technology is not in monitoring equipment and environmental conditions, but in "identification". That is to do corresponding processing by actively identifying objects that enter the magnetic field identification range. RFID is not a sensor, it mainly identifies markers through the unique ID number corresponding to the tag. The sensor is a detection device that can feel the measured information, and can transform the detected information into electrical signals or other required forms of information output according to certain rules, so as to meet the needs of information transmission, processing, and storage. , display, recording and control requirements. It is the first link to realize automatic detection and automatic control.
2. Composition and working principle of radio frequency identification system
1. Composition of radio frequency identification system
The RFID system mainly consists of three parts: tags, antennas, and readers. In addition, a special application system is required to deal with the reader identification accordingly.
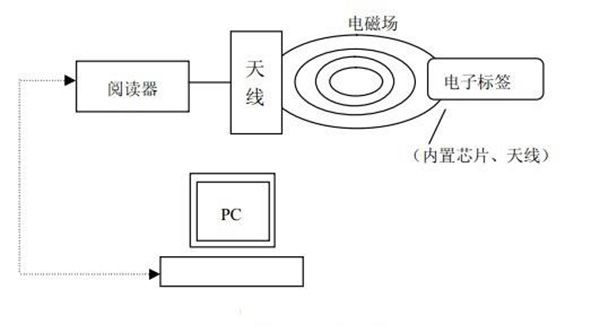
Figure 1 RFID system by composition
1) Tag: electronic tag or radio frequency tag, transponder, composed of a chip and a built-in antenna. Electronic data in a certain format is stored in the chip as the identification information of the item to be identified, and it is the data carrier of the radio frequency identification system. The built-in antenna is used for communication with the RF antenna.
2) Reader: A device that reads or reads/writes electronic tag information. The main task is to control the radio frequency module to transmit a read signal to the tag, receive the response from the tag, decode the object identification information of the tag, and link the object identification information together. Other relevant information on the tag is transmitted to the host for processing.
3) Antenna: The transmitting and receiving device for transmitting data between the tag and the reader.
2. The operating principle of radio frequency identification system
After the electronic tag enters the antenna magnetic field, if it receives a special radio frequency signal from the reader, it can send out the product information (passive tag) stored in the chip by virtue of the energy obtained by the induced current, or actively send a signal of a certain frequency (active tag), the reader reads and decodes the information, and sends it to the central information system for relevant data processing.
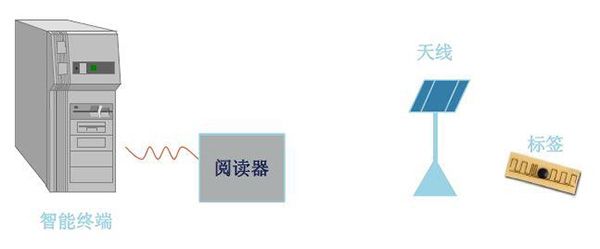
Figure 2 The reader obtains read and write instructions
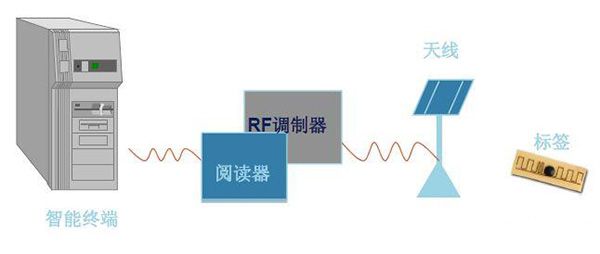
Figure 3 The reader RF modulator sends the signal to the antenna
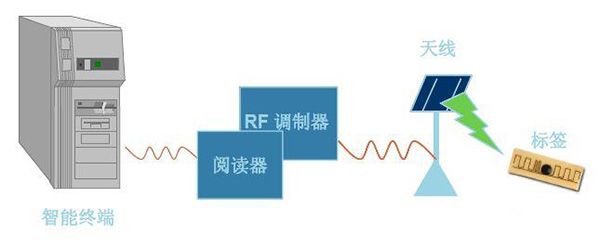
Figure 4 Antenna interrogation label
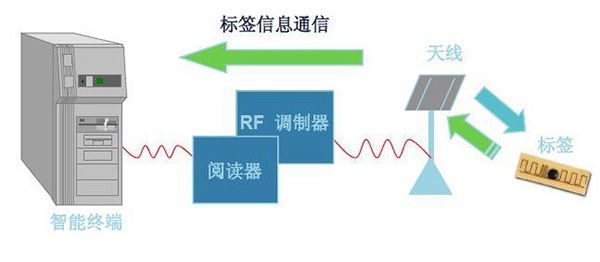
Figure 5 The antenna returns the tag information obtained
In addition, according to the coupling mode of the radio frequency signal between the reader and the tag, the communication between them can be divided into: inductive coupling and electromagnetic backscatter coupling.
1) Inductive coupling: According to the law of electromagnetic induction, the coupling is realized through the spatial high-frequency alternating magnetic field. The inductive coupling method is generally suitable for short-range RFID systems working at medium and low f requencies.
2) Electromagnetic backscatter coupling: According to the spatial propagation law of electromagnetic waves, the emitted electromagnetic waves are reflected after hitting the target, thereby carrying back the corresponding target information. method is generally suitable for long-distance RFID systems that work at high frequencies and microwaves.
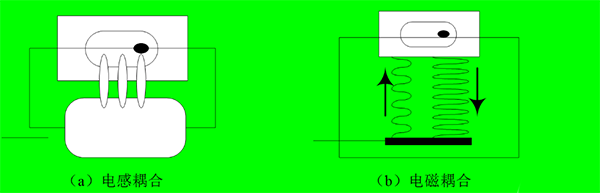
Figure 6 Comparison of two coupling methods
Popular understanding, the inductive coupling mode is mainly used in the low frequency (LF) and intermediate frequency (HF) bands. Since the wavelength of the low frequency RFID system is longer and the energy is relatively weak, it mainly relies on short-distance induction to read information. Electromagnetic backscatter coupling is mainly used in high frequency (HF) and ultra high frequency (UHF) bands, because the wavelength of high frequency is shorter and the energy is higher. Therefore, the reader antenna can radiate electromagnetic waves to the tag, and part of the electromagnetic wave is reflected back to the reader antenna after being modulated by the tag, and then sent to the central information system for receiving and processing after being decoded.
3. RFID and Internet of Things
RFID is an important supporting technology for the Internet of Things to perceive the outside world. Sensors can monitor and sense various information, but lack the ability to identify items, while RFID technology just has a strong ability to identify items. Therefore, for the development of the Internet of Things, both sensors and RFID are indispensable.
Without the ability of RFID to identify objects, the Internet of Things will not be able to realize the highest ideal of the Internet of Everything. Without the support of RFID technology, the scope of application of the Internet of Things will be greatly limited. But on the other hand, since RFID radio frequency identification technology can only realize the identification of objects within the magnetic field range, its reading and writing range is affected by the distance between the reader and the tag. Therefore, improving the sensing capability of the RFID system and expanding the coverage capability of the RFID system is an urgent problem to be solved at present. At the same time, considering the long effective distance of the sensor network, it can well expand the application range of RFID technology. In the future, it will be an inevitable direction to realize the integration of RFID and sensor network.
As far as the current development of RFID is concerned, the initial integration of RFID and sensor network applications has been achieved in many industrial industries. The complementary advantages of the two are deepening the application of the Internet of Things. Their mutual integration and system integration will greatly improve Promoting the development of the entire Internet of Things industry, the application prospects are immeasurable.
Proposal recommendation
- TOP



