- Home >> Solution >> Appliances >> home appliances
Electric water heater solution
According to national standards, electric water heaters can be divided into storage electric water heaters and instantaneous electric water heaters. Instantaneous electric water heaters are mostly used in public places because of their large power consumption. Water storage electric water heaters are divided into closed type, tank water supply type, open outlet type and open type. Household electric water heaters are generally of two types, the closed type and the open type in the storage type electric water heater, and the former is the main type.
1. Technical introduction of electric water heater scheme
1.1 Liner technology
The core technology of electric water heater manufacturing is inner tank technology, which is subdivided into inner tank material, anti-corrosion technology and inner tank processing technology. At present, the electric water heaters on the domestic market are divided into two camps according to the tank technology, the stainless steel tank represented by Haier and the enamel tank represented by Ariston. The advantage of the stainless steel liner is that the material is better and the weight is lighter. The disadvantage is that it has low pressure resistance and is not resistant to impact, especially the weld is easy to leak. However, the production process of the stainless steel liner is simple and the investment in equipment is small, so it is adopted by most domestic manufacturers. Some foreign brand manufacturers such as Ariston have adopted the enamel liner made of imported thickened special steel plate, which has excellent anti-corrosion performance, can withstand internal pressure of more than ten kilograms, has a long service life and is extremely safe, but the production of enamel liner The equipment investment is huge, the process is complex and the technology content is high. With the intensification of market competition, enamel liner technology will become the leading technology of electric water heaters.
1.2 Safety performance, thermal insulation performance and thermal efficiency
The main technology corresponding to the safety performance is the water and electricity separation technology. This is mainly reflected in the manufacturing technology of the heating tube. At present, famous brand electric water heaters in the domestic market generally use golden hook heating tubes. The main material of existing heating tubes generally adopts copper tubes and special stainless steel tubes, with the latter being the main material. The isolation method generally uses magnesium oxide powder as a hydroelectric isolation body. As an auxiliary and a marketing method for water and electricity isolation technology, some manufacturers have installed leakage protection devices and water outlet power-off devices on electric water heaters.
Another technology related to safety performance is the thermostat manufacturing technology. A good thermostat can prevent the water temperature from being too high and avoid scalding accidents. The temperature controllers used in electric water heaters can be divided into two categories: mechanical temperature control and electronic temperature control, and the mechanical temperature control is the leading one. At present, domestic brand-name electric water heaters all use imported thermostats.
Corresponding to the insulation performance is the selection of insulation materials and processing technology for electric water heaters. The choice of material is determined in part by manufacturing techniques, and there are three main categories: polyurethane foam, polypropylene foam, and fiberglass wool. Among them, polyurethane foam has the highest density and the best thermal insulation performance.
The thermal efficiency of an electric water heater is a comprehensive indicator. Thermal efficiency is closely related to heater quality and insulation quality. The denser and thicker the insulation material, the better the insulation performance, and the better the insulation performance, the higher the thermal efficiency. At the same time, the higher the efficiency of the heating tube, the higher the thermal efficiency of the whole machine.

2.The purchase suggestion of electric water heater
2.1 Selection of instant heating and water storage
Household electric water heaters are divided into instant heating type and storage type. Compared with gas water heaters, electric water heaters have the advantages of safety, sanitation, and convenience. Hot water can be provided at any time, and the water temperature is easy to adjust. The instant water heater is small in size and does not need to be preheated, but it has a large power, usually above 4-6kw, and the working current is as high as 20A. It is difficult to be widely used due to the limitation of domestic residential wiring. Furthermore, the instant electric water heater is heated during the flow of water, also known as the over-flow water heater, so it is easily affected by the water pressure during use, and the water temperature changes. The storage-type water heater is heated by volumetric water storage, which can automatically keep warm and maintain a constant temperature. It can also provide hot water during a power outage, and can be used as a domestic hot water supply center to use warm water in multiple places in the family. warm up.
2.2 Choice of closed and open
Storage-type electric water heaters are divided into two types: closed type and open type. The inner wall of the open electric water heater has no pressure resistance requirements, no heat preservation, and the structure is relatively simple, and it cannot supply water to multiple places at the same time; the inner liner of the closed electric water heater can withstand pressure, and the structural design is relatively safe and reasonable. Simultaneously supply water to multiple places. At present, most users choose the closed type.
2.3 Choice of liner
The inner tank of the storage type electric water heater is used to store water. It must have the characteristics of heat preservation, pressure resistance, no rust, no scale, and no water seepage. Otherwise, once damaged, it is difficult to repair, so the life of the electric water heater depends on the inner tank. The material and production process of the tank, and when the user buys an electric water heater, choosing a good liner is the key. At present, the inner tank of electric water heaters on the market mainly includes the following types: galvanized steel inner tank: the inner tank of this zinc protective layer is thinner, easy to form and easy to process, but it is easy to rust after long-term use, which affects the service life. So it is generally not used. Stainless steel liner: stainless steel is better than galvanized sheet in terms of material, and it is not easy to rust; many water heater liners use this material, but the disadvantage is that it is difficult to find weld defects in the stainless steel liner, which is easy to cause hidden dangers. , Chromium in stainless steel will be corroded by chloride ions in tap water and cause weld leakage. Hot-dip galvanized coated anti-rust resin liner: During the processing of the liner, the zinc alloy protective layer formed by the hot-dip galvanizing process has a thickness of more than 0.7 mm, which can prevent rust, touch, and electrolysis, but the quality and life of the liner Depends on the workmanship and quality of zinc alloy and anti-rust resin. Enamel liner: The surface enamel of this liner is made of non-metallic material, which is neither rust nor scale; the liner itself is made of thick steel plate, which has strong pressure resistance, certain impact resistance and good anti-corrosion performance. Therefore, the reliability of the enamel liner is relatively better.
2.4 Choice of outer body shape
The inner pots of early electric water heaters had a variety of shapes, but from a geometric point of view, the round tank-shaped design is the most uniform in force and can withstand high pressure the most. After more than 20 years of development, some well-known brands of water heaters in the market are designed in the shape of a round tank.
2.5 Selection of capacity and power
Generally, 30-40 liters is more suitable for a family of 3, and 60-80 liters is suitable for 4-5 people; the heating power of the storage type electric water heater is generally 1-1.5KW, so the electric meter (electrical load capacity) of the home is required Preferably greater than 10A. Now some electric water heaters have been designed as dual-power heating, which provides users with a choice, and at the same time, it also provides convenience for large-capacity water heaters due to long-term heat preservation needs.

3. Structural composition of instant water heater
The structure of the water heater mainly includes three parts: the heating cylinder, the circuit board, the casing and the accessories.
3.1 Heating cylinder
The heating cylinder is the core component of the water heater and a place for heat exchange. Multiple sets of heating tubes are installed in the cylinder, and electrodes are drawn from the top of the cylinder. A water flow sensor is provided on the water inlet channel (the gear switch is a water flow switch), and a temperature sensor is installed on the water inlet and water outlet channels. The heating cylinder has a diameter of 5cm and a length of 24.5cm, and 4 U-shaped heating tubes are squeezed out. The actual volume is less than 300ml, so the water flow can quickly heat up and realize "instant heat and use".
A temperature control switch is installed on the body of the barrel, the function is to cut off the power when the temperature is over, and the operating temperature is 98°C. In order to ensure effective contact between the bottom of the temperature control switch and the heating cylinder, the contact surface is coated with thermal paste (silicon grease) to reduce thermal resistance. Inside the temperature control switch, there is a coin-sized circular bimetal concave-convex piece, the concave-convex distance is about 1 mm, and the convex surface is close to the metal bottom surface of the switch. , push the transfer rod to push the conductive beam of the switch away from the contact, thus cutting off the circuit. Manual reset is required after action.
Over-temperature can occur in the three states of full water, water shortage or no water in the cylinder. The heat is transferred to the cylinder body through water, water vapor or the top of the cylinder body. The temperature of the upper part of the cylinder body rises fastest, so the temperature control switch is also installed in the upper part. According to this analysis, this type of water heater should be installed vertically.
3.2 Control circuit board
There are two circuit boards, one is the main circuit board, which is directly fixed on the casing, and the other is the display and operation circuit board, which is fixed on the front panel, and the two are connected by a multi-strand cable. After consulting the information, comparing the real objects, and ignoring some circuit details, the logic block diagram of the circuit can be sorted out as follows.
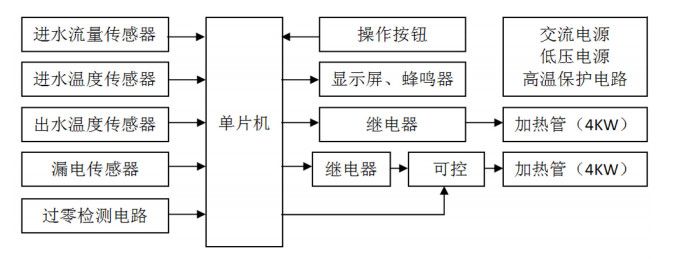
First analyze the heating tube circuit, the heating tube is switched on and off using a relay to achieve strong and weak current isolation. The thyristor device in the second circuit is also directly connected in series in the heating tube circuit, so an optocoupler device is used to realize electrical isolation. The optocoupler sends the control signal of the single-chip microcomputer to the thyristor through the secondary conversion of "electricity-optical-electricity". Followed by the microcontroller control circuit. For the sake of confidentiality, the manufacturer has erased the model identification of the single-chip microcomputer, but it does not affect the analysis of the circuit. The input signal of the single-chip microcomputer includes the water inlet flow rate, the water inlet temperature, and the water outlet temperature, which are provided by the corresponding sensor circuit. The output control signal of the single-chip microcomputer includes two relays and one thyristor. The single-chip microcomputer also uses multiple I/Os to connect circuits such as the display screen, buzzer, E2 PROM memory, and operation buttons. In addition, there are power supply circuit, leakage protection circuit, zero-crossing detection and other circuits.
4.The heating tube circuit analysis of the water heater
4.1 The heating circuit control mode of the shifter
The gear machine is equipped with four heating tubes, the power of which is two 1.7kW and two 2.3kW, respectively controlled by four relays, and a total of 8 power combinations of 1.7-8kW can be combined, corresponding to 8 gears. To suit different temperature needs.
4.2 Control mode of heating circuit of constant temperature machine
The constant temperature machine also has four heating tubes, each 2kW, divided into 2 groups of wiring, each group 4kW, the first group is responsible for "coarse adjustment" by relay control, and the second group is responsible for power "fine adjustment" by relay plus bidirectional thyristor series control ". Thyristor is a high-power semiconductor device, the current can be controlled by changing the conduction angle, and any power distribution between 0-4kW can be realized. The combination of the two groups can realize the output of any power value from 0 to 8kW.
4.3 SCR control principle
Understand the working principle of thyristor control, you can understand more design details of the circuit. The bidirectional thyristor is a multilayer semiconductor device, which is equivalent to a special switch. It is characterized by "triggering on, holding after turning on, and turning off after power off". The T1 and T2 electrodes are connected in series in the heating tube circuit, and the trigger signal It is output by the microcontroller and loaded to the gate G after being isolated by the optocoupler.
After the thyristor is triggered and turned on, even if the trigger signal is removed, the device can remain in the on state until the power is turned off, waiting for the next trigger. The power-off uses the "zero-crossing" of the 50Hz sine wave of the AC power supply. In half a cycle (angle π, duration 10ms), let t1 and t3 be the two "zero-crossing" moments at the beginning and the end, and t2 is a certain loading drive signal , then the angle between t2 and t3 is the conduction angle, as long as the conduction angle (0-π) is changed, the conduction current can be controlled, thereby realizing any power distribution between 0-100%. The single-chip microcomputer samples the zero-crossing signal at time t1, starts timing, and sends a trigger signal when the time delay reaches t2. The size of the conduction angle and its calculation period need to be determined based on complex automatic control theory. The zero-crossing signal comes from the secondary voltage of the power transformer. After being rectified and shaped, it is sent to the single-chip microcomputer as a synchronous control signal.
4.4 Over-temperature protection circuit
There are two groups of over-temperature protection circuits: the first group uses a temperature control switch to prevent abnormal high temperature. The second group of over-temperature protection is "high water temperature protection", and the protection value is generally set to 60°C, which is controlled by the single-chip microcomputer software. , Once over temperature, cut off the heating tube circuit, give display and sound prompts, when the temperature returns below the set value, it will automatically resume normal constant temperature control. During the test, when the water temperature was greater than 60°C, it was observed that the single-chip microcomputer cut off the two relays, turned off the trigger signal of the thyristor, and the buzzer produced three short alarm sounds of 90ms long.
The constant temperature machine uses a variety of sensors such as temperature sensors, flow sensors, current transformers, and temperature control switches. The temperature control switch is both a sensor and a controller. Current transformers are used for leakage protection. The principle and technology of temperature sensor and flow sensor are introduced here.
The water temperature sensor uses an NTC thermistor, and NTC is a negative temperature coefficient. This type of sensor is made of metal oxides such as manganese, cobalt, nickel and copper as the main material, and is manufactured by ceramic technology. At low temperatures, the number of carriers (electrons and holes) in these oxide materials is low, so their resistance is high. As the temperature increases, the number of carriers increases and the resistance value decreases. The resistance value of the temperature sensor needs to be converted into a voltage by the single-chip microcomputer AD conversion, and then converted into a temperature value before it can be used for calculation, control and display.
The internal structure of the water flow sensor is viewed from the top. In the cylindrical internal space, an impeller is placed. The impeller is covered with a magnetic ring, and then sealed with a top cover. The top cover has a groove, which is just embedded in the Hall device, so that the magnetic The distance between the ring and the Hall device is less than 3mm. The water flow drives the impeller to rotate. Using the Hall effect, the element senses the change of the magnetic pole signal and outputs an electrical signal. The Hall effect refers to the phenomenon that when a current flows through a semiconductor sheet, an electromotive force will be generated in a direction perpendicular to the current I and the magnetic field B. The device model is W12, which integrates Hall elements and signal processing circuits, including reference voltages, amplifiers, Schmitt triggers and drive output transistors, and can directly output shaped pulse square waves.

5. The temperature control circuit of the water heater
According to the automatic control theory, typical temperature control generally uses PID analog control, that is, "proportional (P)-integral (I)-differential (D)", where r(t) is the given value, and y(t) is the actual output value , Deviation e(t)=r(t)-y(t), the deviation value is calculated by PID and combined linearly to form a control variable u(t) to control the controlled object.
Proportional control is to output the control quantity proportionally according to the size of the error, so that the controlled quantity changes in the direction of reducing the error, and the size of the control quantity depends on the proportional coefficient Kp. Assuming that the set temperature is 40°C and the proportional bandwidth is 20°C, when the outlet water temperature is below 30°C, the controller will output full power, and above 50°C will output zero, and between the two will be controlled proportionally. In theory, proportional control can achieve constant temperature effect.
However, proportional control cannot solve the problem of static error (also called static error or steady-state error), so integral control is introduced to memorize and integrate the static error, and the generated control quantity is adjusted in the direction of reducing the static error. Integral control needs to integrate the first few error samples before generating a control signal, so there is a large hysteresis, so differential control is introduced. The differential reflects the change trend (change rate) of the error, so as to generate the control amount in time. The temperature value in the actual system is a discrete value obtained by sampling, and the integral and differential items need to be discretized.
Another widely used automatic controller is the fuzzy controller, which is very suitable for tankless water heaters. Research shows that fuzzy control has a better control effect on nonlinear and time-varying uncertain systems. The control process of the fuzzy controller is: after the input signal is processed by the fuzzy interface, the logic stored in the database and rule base is called by the inference engine, and the data vector is used to solve the simulation equation according to the relevant rules to obtain the fuzzy control quantity, and then through the fuzzy interface converted into electrical control signals. Among them, the membership degree vector values of all fuzzy subsets of each input and output variable are stored in the database, and the control rules are stored in the rule library, which are defined by experts and experience. In Yu Hongjie's comparative test, fuzzy control is superior to PID control mode in indicators such as time to reach steady state, control accuracy and anti-interference ability.
6. Safety technical design of water heater
Safety is the primary consideration for users to choose. If the heating tube is broken or perforated, the heating wire in the tube will be in contact with the water, causing the water body to be charged. The instant water heater adopts the following measures to ensure the safe use of electricity.
6.1 Earthing device and leakage protector
A standardized power distribution environment is a barrier for safe use, including grounding systems and leakage protectors. The ground wire in the water heater power cord must be reliably connected to the household ground wire, and the leakage protector should be tested once a month by pressing the test button. The instantaneous water heater has a large power, so it should be equipped with a 40A circuit breaker and a dedicated power line of at least 4mm2 should be laid.
6.2 Leakage detection circuit
There is a special leakage protection circuit inside the water heater. There is a transformer on the power supply line (phase line and neutral line, excluding the ground wire), and a coil is wound on the transformer as the primary coil. The secondary coil of the transformer has a More than a thousand turns. If leakage occurs, the current of the phase line and the neutral line are inconsistent, resulting in magnetic induction, and the secondary induced voltage. After the CS54123 chip circuit is amplified, the single-chip microcomputer controls the water heater to disconnect the relay. In the simulated leakage test, it was observed that the single-chip microcomputer turned off the trigger signals of the 2-way relay and the thyristor after 77 milliseconds, and generated an audible alarm signal and a fault code display.
6.3 Firewall
The anti-electric wall is actually a section of insulating water pipe, which attenuates the leakage current through the resistance of the water body itself. In order to achieve a sufficient length, the internal design is generally a spiral pipe, and the use of this pipe has good reliability.
The above are the details of the water heater solution introduced by Shenzhen Zuchuang Microelectronics Co., Ltd. for you. If you have electronic function development needs for electric water heaters, you can rest assured to entrust them to us. We have rich experience in customized development of electronic products, and can evaluate the development cycle and IC price as soon as possible, and can also calculate PCBA quotations. We are a number of chip agents at home and abroad, including MCU, voice IC, Bluetooth IC and modules, wifi modules. Our development capabilities cover PCB design, single-chip microcomputer development, software custom development, APP custom development, WeChat official account development and other hardware and software design. It can also undertake the research and development of smart electronic products, household appliances scheme design, beauty equipment development, Internet of Things application development, smart home scheme design, TWS scheme development, Bluetooth audio development, children's toy scheme development, and electronic education product development.
- TOP
