China Mobile issued a clear signal of 2G frequency reduction and network withdrawal, and NB-IoT will
Recently, a document issued by the Ministry of Planning and Construction of China Mobile spread on the Internet and caused heated discussions. The focus mainly came from the plan to "decided to stop adding new 2G IoT users before the end of 2020."
The resolution “Decided to stop adding new 2G IoT users before the end of 2020” officially conveys a very clear attitude towards 2G IoT at least at the official level. This attitude will drive the industry to make new decisions. Stopping the addition of 2G IoT will directly pave the way for the development of NB-IoT to a large extent. China Mobile's decision will undoubtedly bring greater breakthroughs to the accelerated development of the NB-IoT industry.
Turn off the water inlet of the 2G IoT “pool”
If the connection of the 2G Internet of Things is compared to a "pool", if the 2G network is to be withdrawn from the network, the water in the "pool" of the 2G connection must be drained. However, each pool has a water inlet and a water outlet. If you want to drain the water in the pool quickly, on the one hand, you need to reduce the speed of water inflow or even close the water inlet. On the other hand, you need to speed up the speed of water outlet.
Generally speaking, the life cycle of IoT devices is relatively long. At present, the industry has not introduced corresponding measures for large-scale upgrading of existing 2G IoT terminals, so the "water out" of this pool is still very slow. In the past few years, the typical characteristic of the 2G Internet of Things pool is that the speed of "water entering" is faster than the speed of "water leaving". If the status quo is maintained, the water in this pool will never be drained.
From this perspective, the purpose of stopping new 2G IoT connections is to close the water inlet of the 2G IoT pool. Only when the water inlet is turned off will the stock of the 2G IoT pool reach an inflection point and begin to decline. Therefore, it can be said that the decision to stop adding new 2G IoT connections is of great significance.
How big is the water inlet and storage volume of the 2G pool?
Turning off the water inlet of the 2G pool is of great significance, due to the "flow rate" of the water inlet of the 2G pool and the huge stock of the pool. We might as well examine it from public data.
According to the data disclosed in the annual financial reports of the three major operators, the number of IoT connections of the three manufacturers has increased rapidly from a total of 343 million in 2017 to 1.23 billion in 2019. Judging from the comparison of the number of connections among the three companies, China Mobile is in an absolute leading position. By the end of 2019, its number of IoT connections had reached 884 million. Such a huge number of IoT connections is mainly carried by cellular networks such as 2G, 3G, 4G, and NB-IoT.
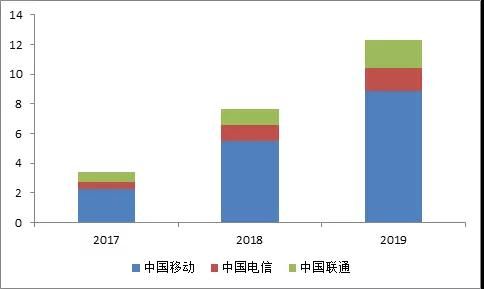
三大运营商物联网用户数(单位:亿,来源:运营商财报,物联网智库)
实际上,业界对于这十多亿物联网连接的结构更为感兴趣,到底哪一类蜂窝网络承载的连接数更多。虽然市场上还没有2G/3G/4G/NB-IoT不同制式物联网连接的数据,但是不同制式物联网连接基本上都对应着不同制式物联网模组,因此我们可以从蜂窝物联网模组的销售量来预判前后一段时间内不同制式物联网连接的结构。
大部分物联网模组企业也没有披露其出货量的结构,然而物联网模组龙头企业移远通信在其财报中披露了不同制式物联网模组的出货量。以移远为例,根据其2019年年报公开数据,我们可以看出不同制式物联网模组销售量如下图所示:
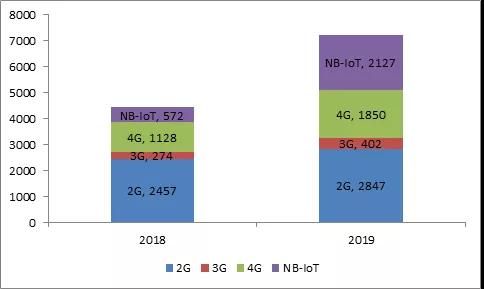
Number of Internet of Things users of the three major operators (unit: 100 million, source: operator financial reports, IoT think tank)
Public data shows that Quectel's sales of 4G and NB-IoT modules have grown rapidly in 2019, but sales of 2G modules are still the highest, reaching 28.47 million units, but its growth rate has been very slow. Let's show it in scale as follows:
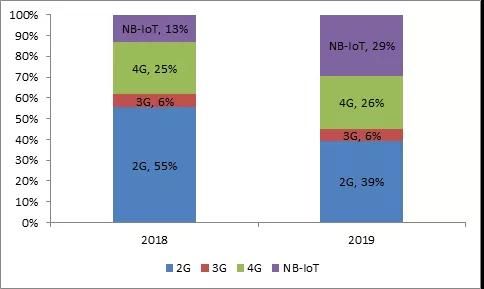
It can be seen that among the four types of modules, 2G/3G/4G/NB-IoT, the number of 2G modules accounted for more than half in 2018, but this number dropped rapidly to 39% in 2019, and NB-IoT modules accounted for more than half. The proportion of the NB-IoT group increased rapidly from 13% to 29%, and the proportion of the other two types of standard modules changed slightly. It can be seen that the increase in the proportion of NB-IoT is basically due to the decrease in the proportion of 2G.
At the beginning of 2017, the Internet of Things Think Tank conducted an in-depth survey of 10 domestic mainstream IoT module companies. The survey results found that 2G IoT module shipments accounted for nearly 80% in 2016. Since it is the result of a survey of 10 mainstream module companies, this number has a certain industry representativeness. During the survey, each module manufacturer stated that 2G modules accounted for a higher proportion before 2016.
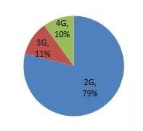
Proportion of IoT modules of different formats in 2016
Although the only publicly available data is IoT think tank survey data and Quectel's shipment data, cross-verification can be performed from different angles, and the data is representative. From a glimpse of the leopard, we may draw some conclusions:
Before 2020, most of the existing and newly added cellular IoT connections come from 2G IoT. As of 2019, the proportion of 2G modules is still much higher than that of other standards, not to mention that the proportion of 2G modules was even higher than before. Module shipments will be reflected in the number of IoT connections after a certain period of time, and the final ratio is roughly synchronized with the module ratio.
It can be seen that the "water pool" of 2G Internet of Things has a very high stock, and the speed of entering the water is also very fast. Although the specific proportion of 2G IoT connections cannot be calculated, based on the previous data analysis, it is certain that more than half of the more than one billion IoT connections are 2G connections. Therefore, in order to speed up the migration of 2G network, it is very important to close the water inlet of 2G IoT from the source.
Close the 2G water inlet, NB-IoT drainage is at the right time
As can be seen from the previous article, by the end of 2019, the shipment volume of 2G modules is still higher than that of other standards. Large-scale shipments mean that there is still strong demand. With the inlet of 2G IoT closed, it is inevitable that 2G modules and new connections will fall off a cliff, but this demand cannot be without an entrance. Just like Dayu 4,000 years ago when he controlled the floods, he could not rely on blocking the raging floods, but only divert them. The closure of the entrance of the 2G IoT pool is the best time to direct these demands to the entrance of the pool of NB-IoT.
Public data shows that as of February this year, the number of domestic NB-IoT connections has reached 100 million, more than 10 million in gas meters, water meters, fire protection, electric vehicle anti-theft and other fields, and there are also a large number of industries with multi-million applications. Many application fields used 2G connections before, but after NB-IoT showed its advantages, NB-IoT was used for new connections, which successfully achieved grooming.
In Zhejiang Telecom’s announcement of the winning bid structure for NB-IoT module procurement this month, the lowest winning bid price for NB-IoT modules has entered the range of 12 yuan, which to a large extent has a cost advantage over 2G modules. Create conditions to divert 2G Internet of Things demand to the new entrance of NB-IoT.
Since the beginning of this year, although Cat.1 has become a hot spot in the IoT circle and has been placed high hopes by many people to undertake 2G IoT connections, the author believes that after the new entrance to the 2G IoT is closed, the number of entrances that can be diverted to Cat.1 Relatively few, an important reason is the cost factor. According to the latest procurement data of Zhejiang Telecom, the lowest price of Cat.1 modules is around 35 yuan. After all, Cat.1 is based on LTE tailoring, which has high complexity, and there is still a long way to go to reduce the cost to the level of 2G modules. However, a large number of 2G Internet of Things users are very cost-sensitive, and the module cost of more than twice is enough to discourage users. Therefore, more 2G Internet of Things demand will be channeled to the water inlet of NB-IoT.
In addition to meeting the needs of 2G at the cost and application levels, 2G infrastructure is also continuing to migrate to NB-IoT. It is very typical that the 2G spectrum is continuously compressed and much of it is used for NB-IoT network deployment after re-farming. This trend can be clearly seen from the refarming of spectrum by the three major operators:
(1) China Telecom’s re-cultivation work: In June 2016, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the “Ministry of Industry and Information Technology No. 193 Document [2016] No. 193” regarding China Telecom’s use of the 800M and 2100M frequency bands for LTE networking. The 800MHz re-cultivation has a policy basis; In July 2016, China Telecom announced the launch of 800M network re-farming to reduce the number of CDMA carriers; after re-farming the 825-835MHz/870-880MHz frequency band, in May 2017, China Telecom announced the completion of the world's first full network coverage. NB-IoT network.
(2) China Unicom’s re-farming work: In December 2016, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued a document agreeing to China Unicom’s adjustment of some frequencies for LTE networking, allowing it to re-farm 900MHz and 1.8GHz across the country. These two frequency bands It is China Unicom's 2G frequency band; under the policy loosening, China Unicom has started the work of 2G frequency reduction and network withdrawal, and deployed 4G and NB-IoT networks in these two frequency bands.
(3) China Mobile’s re-farming work: In April 2018, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued an FDD license to China Mobile and allowed it to start re-farming the 900MHz and 1800MHz frequency bands under the premise of legal compliance. In these two Deploy LTE FDD network on the frequency band; 900MHz is China Mobile's main 2G frequency band. Driven by this policy, China Mobile quickly re-cultivated 900MHz and quickly built 4G and NB-IoT networks.
It can be seen that in terms of network infrastructure, many high-quality frequency resources withdrawn from 2G Network are used for NB-IoT construction, which to a certain extent is also a manifestation of channeling 2G IoT to the NB-IoT entrance.
A key decision in the breakthrough development of NB-IoT
This document from the Ministry of Planning and Construction of China Mobile has aroused heated discussion in the industry. In the author's opinion, this is a very critical decision of China Mobile in promoting the development of NB-IoT, which highlights its determination in the development of NB-IoT. At the same time, In the long run, it will also substantially optimize its IoT connection structure. The significance of this decision can be seen from the analysis of the following aspects.
(1) Pay equal attention to stopping 2G new additions and building high-quality NB-IoT networks
In this document, in addition to the highlight of "the decision to stop adding new 2G IoT users before the end of 2020", the decision to "build 118,000 new NB-IoT base stations nationwide in 2020" deserves more attention.
As analyzed above, China Mobile has decided to stop adding new 2G IoT users, and this new demand will be channeled to the NB-IoT network. China Mobile has the best 2G network in the world, and users migrating from 2G to the network will be taken over by NB-IoT. The network to be taken over should also be a high-quality network to provide users with better services. China Mobile's decision to add 50% of NB-IoT base stations is behind its goal of building a high-quality NB-IoT network.
In May this year, the "Notice on Further Promoting the Comprehensive Development of the Mobile Internet of Things" issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology also mentioned: further increasing the deployment of NB-IoT networks, building new NB-IoT base stations as needed, and achieving universal coverage in urban areas at the county level and above. Coverage, achieving deep coverage for indoor, traffic network, underground pipe network, modern agricultural demonstration areas and other application scenarios. Previously, China Mobile's NB-IoT network has achieved coverage in 346 cities. With the addition of 118,000 NB-IoT base stations this year, it is believed that deeper coverage will be achieved.
(2) Open the road to optimization of mobile Internet of Things connection structure
As of the end of 2019, China Mobile's IoT connections reached 884 million, accounting for more than 70% of the total connections of the three major operators. In 2017, the number of China Mobile's IoT connections was 229 million, an increase of 655 million in two years. This growth rate is absolutely leading among global operators, but the IoT connection structure formed is not reasonable.
From the previous analysis of 2G connections, we can estimate that 2G accounts for the majority of China Mobile’s 884 million IoT connections. Such a structure is contrary to the general trend of 2G network frequency reduction and network withdrawal, and is not conducive to its expansion of the Internet of Things industry ecology and the development of new business models. The 2G network has been carrying IoT connections for a long time, which will lead to a situation where the last one cannot be eliminated in the long run. As a component of 5G mMTC, NB-IoT can carry corresponding IoT users for a long time. In the end, most 2G users will still have to migrate to NB-IoT.
This time, China Mobile proactively proposed to stop adding new 2G IoT users, which can be seen as its initiative to start optimizing the IoT connection structure, further reducing the proportion of 2G IoT in the total IoT connections, and increasing NB-IoT and 4G connections. The proportion is in line with the long-term development trend of the industry, and also creates conditions for China Mobile's innovation based on NB-IoT and 4G Internet of Things.
Since China Mobile occupies an absolute leading position in the number of IoT connections, it has proactively started optimizing the IoT connection structure, which will also change the national IoT connection structure to a certain extent and further accelerate the innovation of China Telecom and China Unicom in this area.
(3) Continue to promote the signal of 2G frequency reduction and network withdrawal, and accelerate the conversion of old and new kinetic energy
Stopping new 2G IoT users and increasing the number of NB-IoT base stations also implies China Mobile’s determination to continue promoting 2G frequency reduction and network withdrawal. In the context of this year's new infrastructure construction, while leading infrastructure construction, it is also necessary to accelerate the withdrawal of old production capacity. 2G frequency reduction and network withdrawal is an important manifestation of the conversion of old and new momentum in the field of Internet of Things.
The 2G network has been in operation for 20 years. Against the background of intergenerational upgrades in mobile communications and the acceleration of 5G commercial use, the shortcomings of the 2G network have become increasingly apparent. For example, the 2G network occupies the golden frequency band, but its resource utilization efficiency is far lower than that of new communication systems; the spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency of the 2G network can no longer meet the requirements of the industry; and the 2G industry ecology has undergone tremendous changes, and many manufacturers have withdrawn from this industry. In the field, the subsequent operation and maintenance cost of the network is too high.
Actively promoting 2G frequency reduction and network withdrawal to develop NB-IoT is to a large extent an important way to improve 5G infrastructure and industrial ecology. As we all know, NB-IoT has been included in the 5G candidate standards, and the NB-IoT network will become an infrastructure component in the future 5G mMTC scenario; NB-IoT supports the needs of digital upgrades in thousands of industries, and currently NB-IoT faces all Users are all the user groups that 5G Internet of Things must cover, forming the pioneers of the expansion of 5G ecology.
This initiative to stop the development of 2G IoT users has once again sent a clear signal to the industry about 2G frequency reduction and network withdrawal. Since China Mobile has the largest 2G network in the world, the clear attitude towards 2G frequency reduction and network withdrawal will undoubtedly provide a clear direction for the development path of the entire Internet of Things industry.
As China Mobile has clearly stopped adding 2G IoT users, the capacity of the 2G IoT pool has begun to enter the downstream channel. The closure of the 2G IoT pool inlet will inevitably pave the way for the expansion of the new inlet of NB-IoT. China Mobile's initiative to clarify its attitude towards 2G IoT is undoubtedly a wise move under the current development environment. It has made a key decision to promote the development of NB-IoT and also opened the way to optimize the overall structure of IoT connections.
Proposal recommendation
- TOP



